Web browsers are the gateways to the digital world, and two of the most widely used options are Mozilla Firefox and Google Chrome. This comparative analysis explores the key features, performance, security, and user experience of Firefox and Chrome, aiding users in making an informed choice based on their preferences and requirements.
Body:
1. **User Interface:**
– **Firefox:** Firefox offers a clean and customizable user interface. Users can personalize the browser through themes and extensions, tailoring the experience to their liking.
– **Chrome:** Chrome features a minimalist design with a focus on simplicity. Its interface is user-friendly, with a unified search and address bar, known as the Omnibox.
2. **Performance:**
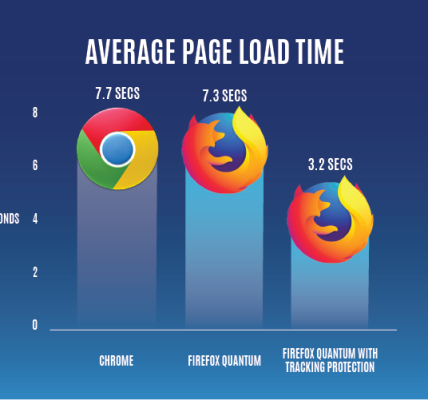
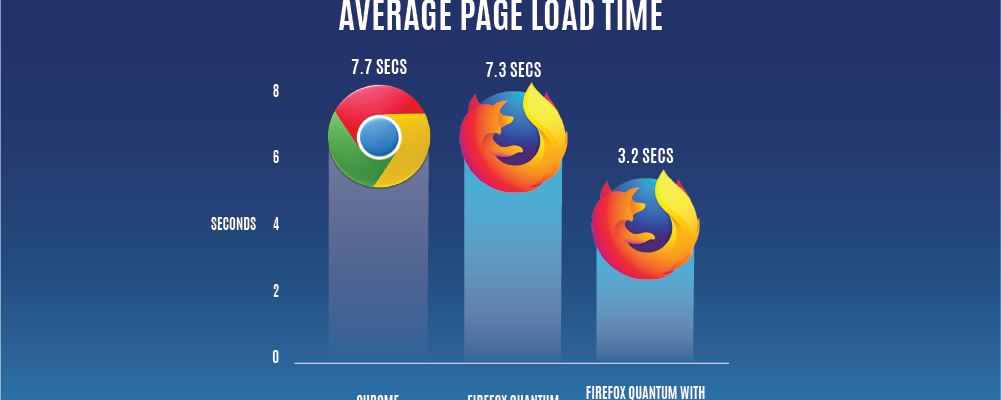
– **Firefox:** Over the years, Firefox has undergone significant performance improvements. Quantum, its redesigned engine, enhances speed and responsiveness, providing a competitive browsing experience.
– **Chrome:** Chrome is recognized for its fast rendering and efficient JavaScript engine (V8). Its multi-process architecture ensures stability even when one tab crashes, minimizing disruptions.
3. **Extensions and Add-ons:**
– **Firefox:** Firefox boasts a vibrant add-ons ecosystem. Users can choose from a wide range of extensions that enhance functionality, privacy, and customization.
– **Chrome:** The Chrome Web Store offers an extensive collection of extensions. Chrome’s large user base attracts developers, resulting in a diverse selection of add-ons.
4. **Privacy and Security:**
– **Firefox:** Mozilla emphasizes user privacy and security. Firefox includes enhanced tracking protection, strict anti-phishing measures, and a privacy-focused browsing mode.
– **Chrome:** Chrome utilizes Google Safe Browsing to warn users about potentially harmful websites. While it has robust security features, some users may have concerns about data collection given Google’s business model.
5. **Cross-Device Syncing:**
– **Firefox:** Firefox Sync enables users to sync bookmarks, history, passwords, and open tabs across devices. It prioritizes user privacy by employing end-to-end encryption.
– **Chrome:** Chrome Sync offers seamless integration with a Google account, syncing browsing data across devices. While convenient, users should be mindful of potential privacy implications.
6. **Customization Options:**
– **Firefox:** Firefox provides extensive customization options, allowing users to tailor the browser to their preferences. This includes themes, toolbar configurations, and the ability to customize new tab pages.
– **Chrome:** While Chrome offers some customization options, they are more limited compared to Firefox. Users can personalize themes and arrange bookmarks but with fewer options for overall interface customization.
7. **Resource Usage:**
– **Firefox:** Firefox has made strides in optimizing resource usage. Quantum’s improvements include better memory management, resulting in a more efficient browser.
– **Chrome:** Chrome’s multi-process architecture can lead to higher memory usage, especially with numerous open tabs. However, Google continually works on optimizing resource consumption.
8. **Offline Browsing:**
– **Firefox:** Firefox supports offline browsing through extensions and the ability to save web pages for offline viewing. Users can access previously visited pages without an internet connection.
– **Chrome:** Chrome allows users to save pages for offline viewing and provides offline versions of certain Google services. However, the extent of offline functionality may vary depending on the website.
9. **Compatibility:**
– **Firefox:** Firefox is compatible with a wide range of websites and web standards. The browser’s commitment to open standards ensures compatibility with various online platforms.
– **Chrome:** Chrome, being developed by Google, is optimized for Google services and tends to work seamlessly with many popular websites. Some users may experience enhanced compatibility with Google products.
10. **Developer Tools:**
– **Firefox:** Firefox Developer Tools offer a comprehensive set of features for web developers. The browser supports technologies like WebAssembly and provides tools for debugging, inspecting, and profiling web applications.
– **Chrome:** Chrome Developer Tools are widely praised for their versatility. They include powerful debugging features, a robust JavaScript console, and performance analysis tools, making it a preferred choice for many developers.
Conclusion:
The choice between Firefox and Chrome ultimately depends on individual preferences, priorities, and the desired user experience. Firefox excels in customization and privacy, while Chrome offers seamless integration with Google services and efficient performance. Users should consider their specific needs, including privacy concerns, extension preferences, and interface customization, to determine which browser aligns best with their browsing habits and priorities.
![Firefox vs Chrome 2024 [Mozilla vs Google Browser Showdown]](https://www.cloudwards.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/firefox-vs-chrome-1.png)