Mozilla Firefox, an open-source web browser, has been a stalwart in the world of internet browsers, championing user privacy and promoting an open web. This article delves into the architecture and development of Mozilla Firefox, exploring the key components that make it a popular choice among users seeking a secure and customizable browsing experience.
Body:
1. **Gecko Rendering Engine:**
At the heart of Firefox lies the Gecko rendering engine, responsible for rendering web pages and displaying content. Gecko is known for its adherence to web standards and its focus on providing a fast and reliable browsing experience. It interprets HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to render the visual elements of web pages.
2. **Quantum Project:**
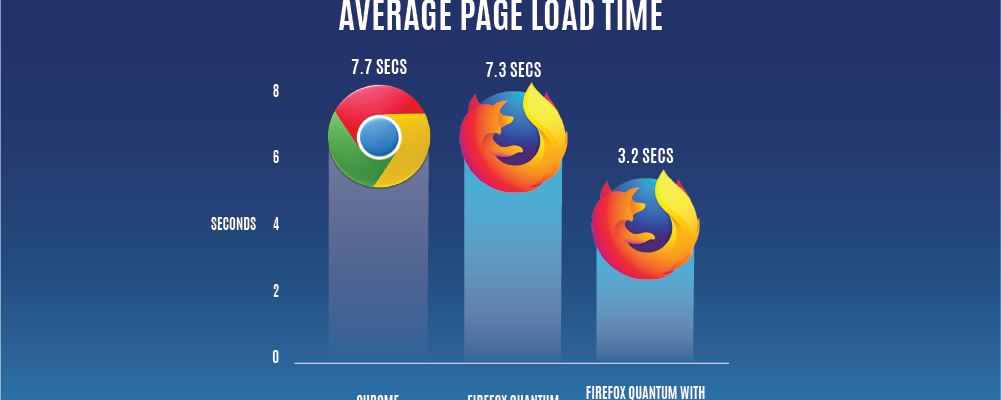
The Quantum project, introduced in Firefox 57, brought significant improvements to the browser’s performance and responsiveness. It included a new CSS engine (Stylo), a redesigned multi-process architecture, and enhancements to the JavaScript engine (SpiderMonkey), collectively contributing to a faster and more efficient browsing experience.
3. **Rust Programming Language:**
Firefox incorporates components developed using the Rust programming language. Rust, known for its focus on memory safety and performance, is utilized in critical areas of Firefox to enhance security and prevent common programming errors that could lead to vulnerabilities.
4. **Electrolysis (e10s):**
Electrolysis is the multi-process architecture implemented in Firefox to enhance stability and security. With e10s, different elements of the browser, such as tabs and extensions, run in separate processes. This isolation prevents a single tab or extension from affecting the stability of the entire browser.
5. **WebExtensions API:**
Firefox embraces the WebExtensions API, a cross-browser extension system. This allows developers to create extensions that are compatible not only with Firefox but also with other major browsers. The WebExtensions API simplifies the development and maintenance of browser extensions, promoting a diverse ecosystem.
6. **Privacy and Security Features:**
Mozilla Firefox has been a pioneer in implementing privacy and security features. It was one of the first browsers to introduce a private browsing mode, and it includes features like Tracking Protection to block third-party trackers, Enhanced Tracking Protection for known trackers, and support for the Do Not Track header.
7. **Open Source Community Development:**
Firefox’s development is driven by an open-source community, including contributors from around the world. The codebase is publicly accessible, allowing developers to scrutinize, contribute, and build upon the browser’s foundation. This collaborative approach fosters innovation and ensures a diverse range of perspectives in the development process.
8. **Customization and Themes:**
Firefox is renowned for its customization options. Users can personalize their browsing experience through a vast collection of themes and extensions available in the Mozilla Add-ons repository. This flexibility allows users to tailor Firefox to their preferences and needs.
9. **Servo:**
Mozilla has been working on the Servo project, an experimental browser engine built from the ground up with a focus on parallelism and concurrency. While not yet the primary engine for Firefox, Servo serves as a testing ground for innovative ideas that may influence the future development of Firefox.
10. **Regular Updates and Stability:**
Firefox follows a rapid release cycle, providing regular updates to address security issues, introduce new features, and enhance overall stability. The commitment to continuous improvement ensures that users benefit from the latest advancements and remain protected against emerging threats.
Conclusion:
Mozilla Firefox’s architecture and development reflect a commitment to an open web, user privacy, and constant innovation. From the robust Gecko rendering engine to the Quantum project’s performance improvements, Firefox continues to evolve to meet the changing needs of users in a dynamic digital landscape. The browser’s emphasis on security, customization, and community-driven development positions it as a key player in shaping the future of web browsers.